Containment Settings
- Click
'Settings' > 'Containment' > 'Containment Settings'.
The settings area lets you configure how proactive the auto-containment feature should be, and which types of files it should check.
Configure containment settings
- Click 'Settings' on the XCS home screen
- Click 'Containment' > 'Containment Settings'
- By default, contained applications can access folders, files and registry keys on your local system, but cannot make changes to them.
- Contained apps are also prevented from accessing Component Object Model (COM) and Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) components on your computer
- The settings screen lets you create exceptions to these policies if required.
- You can also allow contained applications to access removable storage like USB sticks and external hard disk drives.
Do not virtualize access to the specified files/folders - Specify files/folders on the host computer that contained applications are allowed to write to. By default, contained applications write to a virtual file system, and cannot access files/folders on the host system.
- Select the option then click 'the specified files/folders' link.
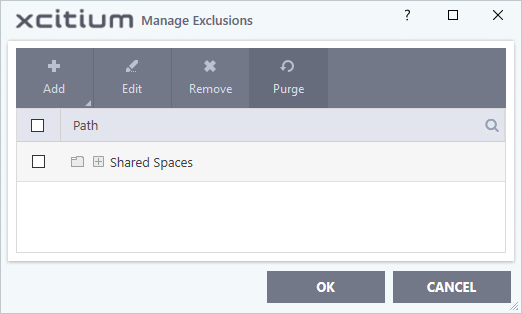
- The 'Manage Exclusions' dialog shows files and folders that can be modified by contained applications. By default, 'Shared Space' is the only folder they can write to:
- Click
the 'Add' button in the 'Manage Exclusions' dialog:
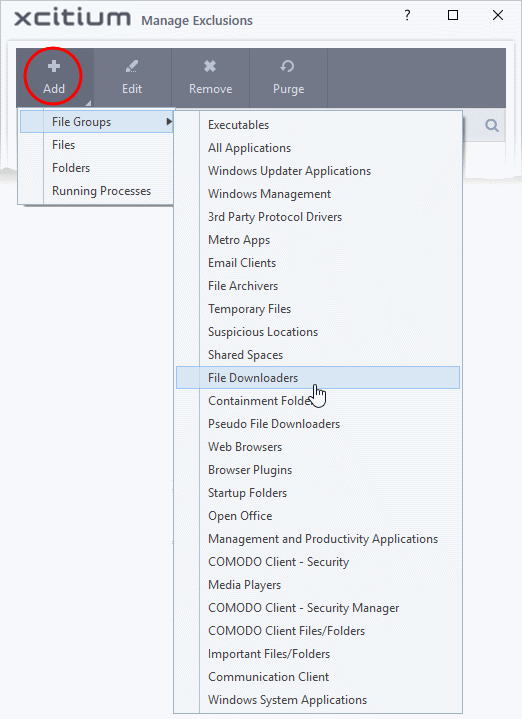
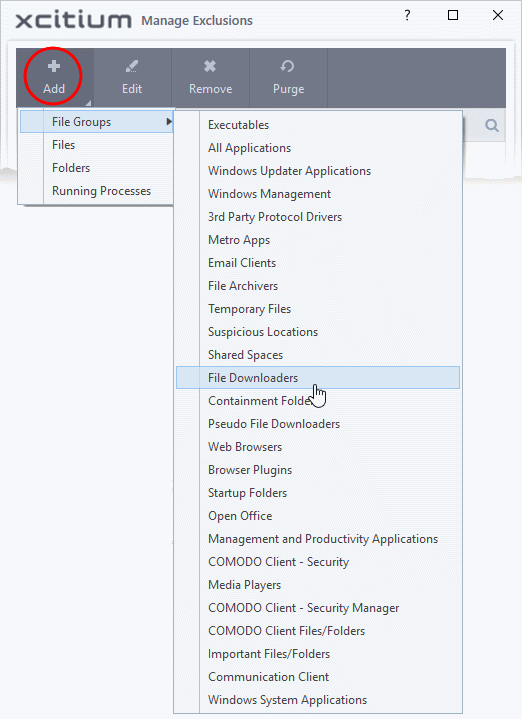
- File Groups - Choose a category of files or folders to which access should be granted. For example, select 'Executables' to create an exception for all files with the extensions .exe .dll .sys .ocx .bat .pif .scr .cpl, */cmd.exe *.bat, *.cmd. See 'File Groups', for more details on file groups
- Files - Pick specific files or applications that contained applications can access
- Folders - Specify folders that can be accessed by contained applications. Access is granted to all files in the folder.
- Running Processes - Choose a process currently running on your computer. The parent application of the process is added to the exclusions.
- Edit - Select an item and click 'Edit' to change the target file or folder
- Remove - Select an item and click 'Remove' to delete an exception
- Purge - Checks that all files and folders covered in exceptions are still present on your computer. Purge automatically removes any items it can no longer locate
- Click 'OK' to implement your settings
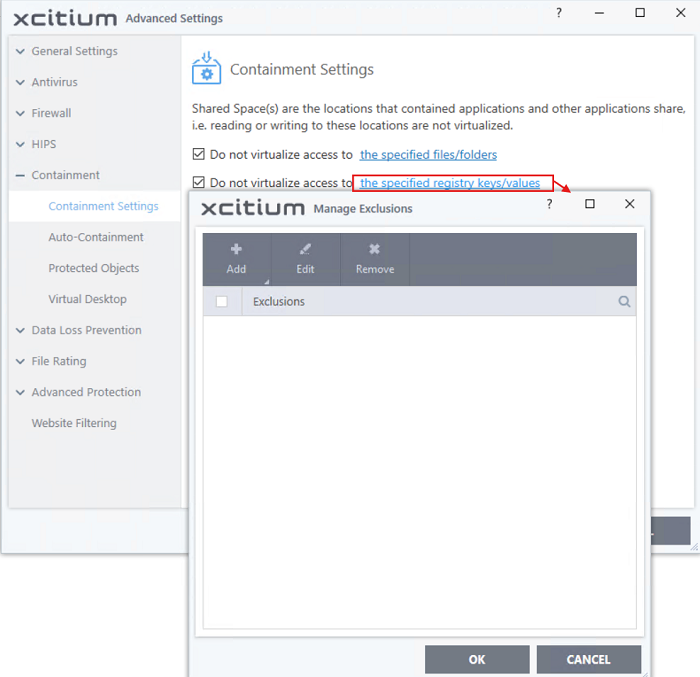
Do not virtualize access to the specified registry keys/values - Specify registry keys on the host computer that contained applications are allowed to write to. By default, contained applications write to a virtual registry, and cannot access the real registry on the host system.
- Select the option then click 'the specified registry keys/values' link.
- The 'Manage Exclusions' dialog shows keys which you have allowed contained applications to access:
- Click
the 'Add' button in the 'Manage Exclusions' dialog.
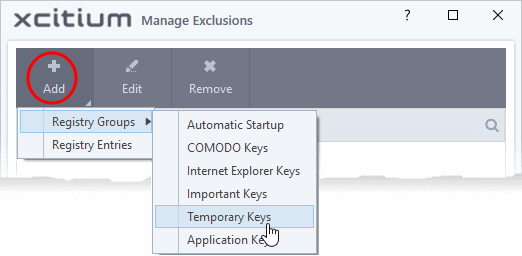
- Registry Groups - Batch select a predefined group of important registry keys as exclusions. See 'Registry Groups' for an explanation of registry groups defined in XCS.
Registry Entries - Browse to individual Windows registry keys and add them as exclusions:
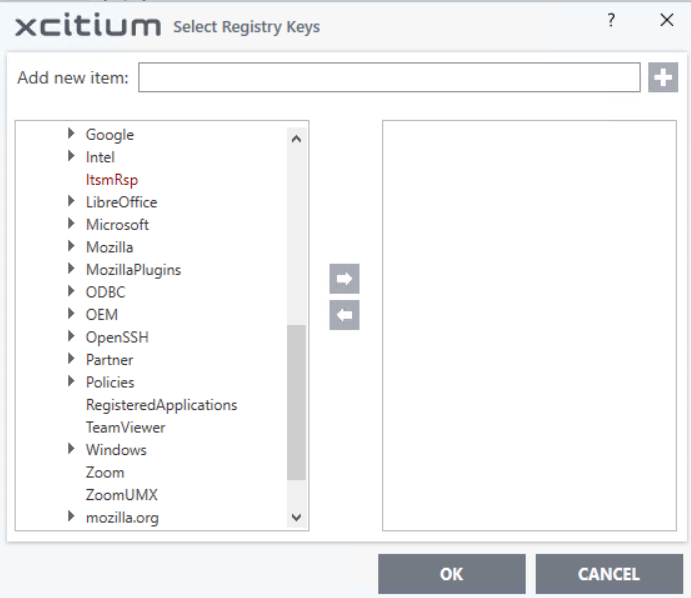
- Edit - Select an item and click 'Edit' to change the target path
- Remove - Select a key or group and click 'Remove' to delete the exception
- Click 'OK' to implement your settings
Do not virtualize access to the removable storage media - Allow contained applications and virtual desktop applications to write to external storage devices. Example devices include USB sticks and external hard drives. (Default = Disabled)
Do not restrict access to COM/DCOM for these applications - By default, contained applications cannot access the COM and DCOM components running on your computer. This setting lets you specify applications that can access COM / DCOM components, even if the app is in the container.
- Select the option then click the 'these applications' link.
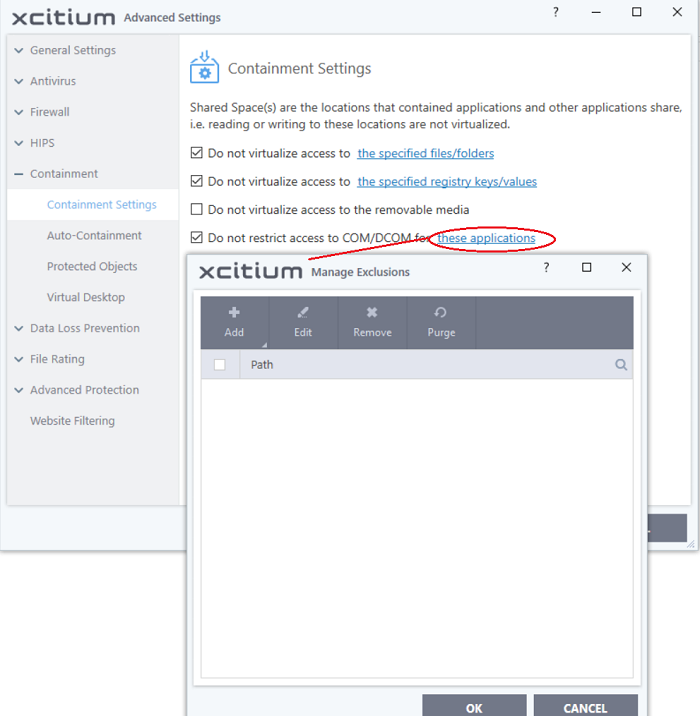
- Click the 'Add' button in the 'Manage Exclusions' dialog.
- File Groups - Choose a category of files or folders to which access should be granted. For example, select 'Executables' to create an exception for all files with the extensions .exe .dll .sys .ocx .bat .pif .scr .cpl, *cmd.exe *.bat, */.cmd. See 'File Groups', for more details on file groups.
- Files - Pick specific files or applications that can access COM / DCOM when run inside the containment.
- Folders - Specify folders as exclusions. Access to COM and DCOM is granted to all files in the folder even if they are run inside the containment.
- Running Processes - Choose a process currently running on your computer. The parent application of the process is added to the exclusions.
- Edit - Select an item and click 'Edit' to change the target file or folder
- Remove - Select an item and click 'Remove' to delete an exception
- Purge - Checks that all files and folders covered in exceptions are still present on your computer. Purge automatically removes any items it can no longer locate.
- Click 'OK' to implement your settings.
Advanced Settings:
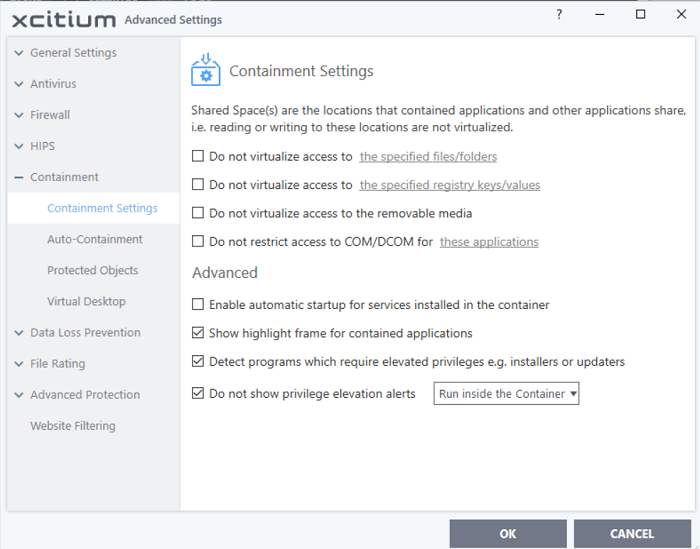
- Enable automatic startup for services installed in the container - XCS launches contained services at Windows startup if this option is enabled. (Default = Enabled)
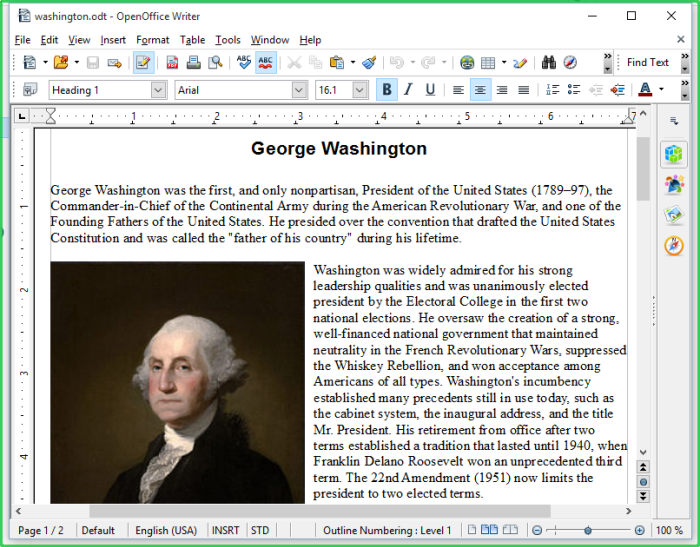
- Show highlight frame for contained applications - XCS displays a green border around the windows of programs that are running in the container. (Default = Enabled)
The following screenshot shows an Open Office document running in the container:
-
Detect programs which require elevated privileges, e.g., installer or updaters: XCS generates an alert when it detects an installer/updater that requires admin/elevated privileges to run. An installer that is allowed to run with elevated privileges can make changes to important areas of your computer such as the registry. (Default = Enabled)
- Example
alert:
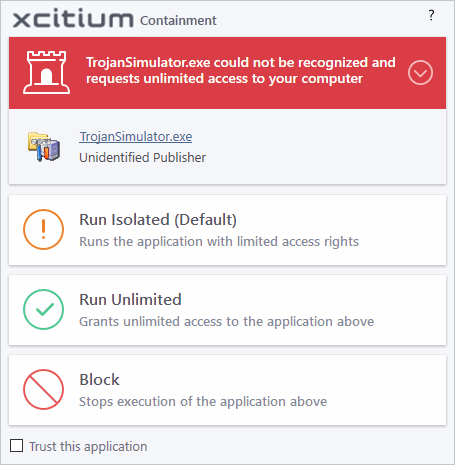
- Run Isolated - Runs the installer/updater in the container
- Run Unlimited - Runs the installer/updater on your local computer, outside the container.
- Block - Terminates the installer/updater.
- See 'Understand Security Alerts' for more details.
Disable this option if you want XCS not to monitor applications that request elevated privileges on your computer
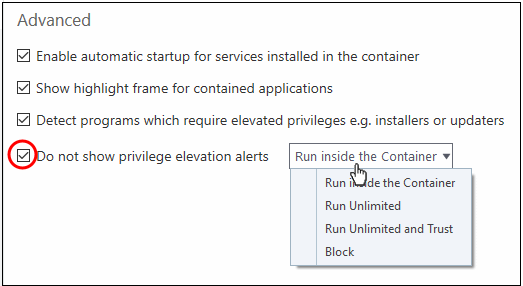
- Do not show privilege elevation alerts: XCS will not show alerts (as shown above) when a new or unrecognized application requires admin or elevated privileges to run.
- If you disable alerts, you need to choose a default action that XCS should implement when it detects such an application:
|
Note. You may see an error if an app on the host tries to update itself at the same time as that app is updating itself in the container. This is a classic Windows sharing violation which is shown when an app attempts to write to a file that is already in use. Please shut down the contained version of the app then run the update on the locally hosted version. The contained version will function correctly once the update to the local version is complete. |