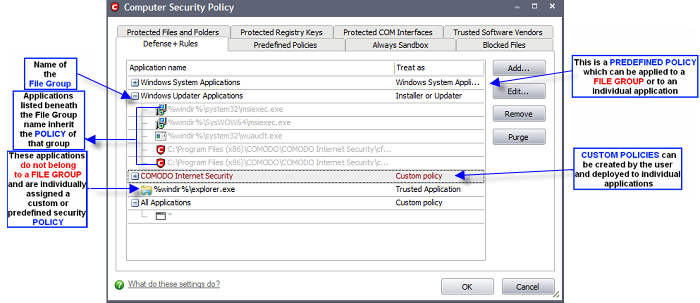
Defense+ Rules
The Defense+ Rules tab lists the different groups of applications installed in your system and the security policies applied to them. You can change the policy applied to selected applications and also create custom policies to be applied to selected applications.
The first column, Application Name, displays a list of the applications on your system for which a security policy has been deployed. If the application belongs to a file group, then all member applications assume the security policy of the file group. The second column, Treat as, column displays the name of the security policy assigned to the application or group of applications in column one.
-
Add... - Allows the user to Add a new Application to the list then create it's policy. See the section 'Creating or Modifying a Defense+ Security Policy'.
-
Edit... - Allows the user to modify the Defense+ security policy of the selected application. See the section 'Creating or Modifying a Defense+ Security Policy'.
-
Remove - Deletes the current policy.
|
Note: You cannot remove individual applications from a file group using this interface - you must use the 'File Groups' interface to do this. |
-
Purge - Runs a system check to verify that all the applications for which policies are listed are actually installed on the host machine at the path specified. If not, the policy is removed, or 'purged', from the list.
Users can re-order the priority of policies by simply dragging and dropping the application name or file group name in question. To alter the priority of applications that belong to a file group, you must use the 'File Groups' interface.
Creating or Modifying a Defense+ Security Policy
To begin defining a application's Defense+ policy
(1) Select the application or file group that you wish the policy to apply to.
(2) Configure the security policy for this application.
(1) Select the application or file group that you wish the policy to apply to
If you wish to define a policy for a new application (i.e. one that is not already listed), click the 'Add...' button in the main Defense+ Rules interface.
This brings up the 'Application System Activity' Control interface shown below.
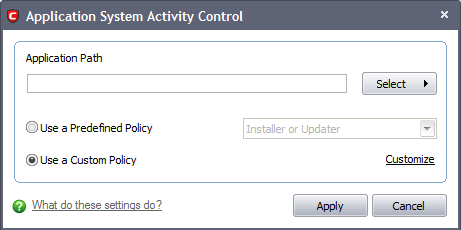
Because you are defining the Defense+ security settings for a new application, you can notice that the 'Application Path' box is blank. (If you were editing an existing policy instead, then this interface would show that policy's name and path.)
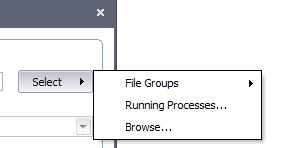
You now have 3 methods available to choose the application for which you wish to create a policy - File Groups; Running Processes and Browse.
-
File Groups - choosing this option allows you to create a Defense+ security policy for a category of pre-set files or folders. For example, selecting 'Executables' would enable you to create a Defense+ policy for all files with the extensions .exe .dll .sys .ocx .bat .pif .scr .cpl . Other such categories available include 'Windows System Applications' , 'Windows Updater Applications' , 'Start Up Folders' etc - each of which provide a fast and convenient way to apply a generic policy to important files and folders.
To view the file types and folders that are affected by choosing one of these options, you need to visit the 'File Groups' interface.
The File Groups interface can be accessed by the following method:
-
Navigate to Defense+ > Computer Security Policy > Protected Files and Folders then click the 'Groups...' button.
-
Running Processes - as the name suggests, this option allows you to create and deploy a Defense+ policy for any process that is currently running on your PC.
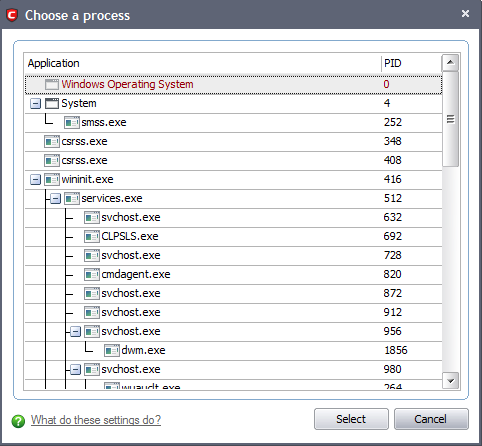
You can choose an individual process (shown above) or the parent process of a set of running processes. Click 'Select' to confirm your choice.
-
Browse... - this option is the easiest for most users and simply allows you to browse to the location of the application for which you want to deploy the Defense+ security policy.
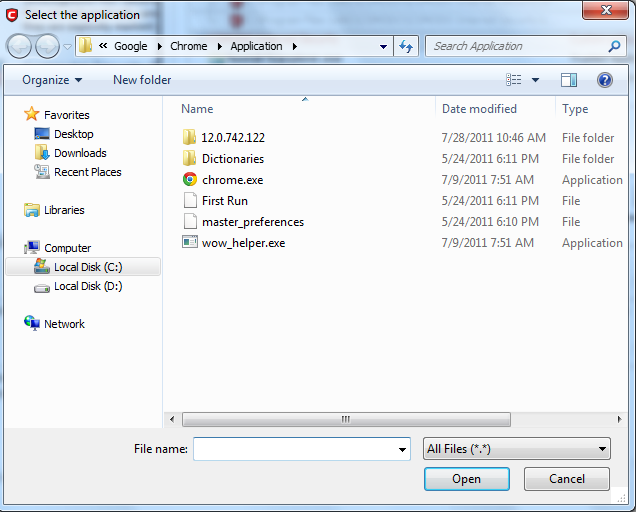
In the example below, we have decided to create a security policy for the Opera web browser.
Having selected the individual application, running process or file group, the next stage is to Configure the rules for this application's policy.
(2) Configure the security policy for this application
There are two broad options available for selecting a policy that applies to an application - Use a Pre-defined Policy or Use a Custom Policy.
-
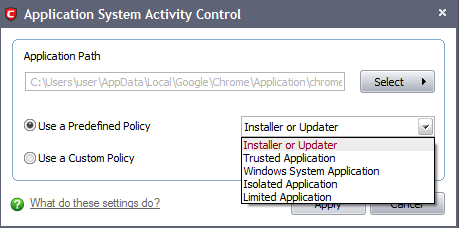
Use a Predefined Policy - Selecting this option allows the user to quickly deploy a existing security policy on to the target application. Choose the policy you wish to use from the drop down menu. In the example below, we have chosen 'Limited Application'. The name of the predefined policy you choose is displayed in the 'Treat As' column for that application in the Computer Security Policy interface (Default = Disabled).
|
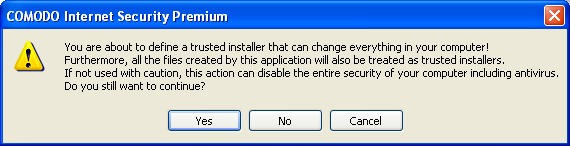
Note on 'Installer or Updater' Policy : Applying the Predefined Policy 'Installer or Updater' for an application defines it as a trusted installer and all the files created by the application will also be considered as as trusted files. Some of the applications may have hidden codes that may potentially impair the security of your computer if allowed to create files of its own. Comodo advises you to use this Predefined Policy - 'Installer or Updater' with caution. On applying this policy to any of the application, an alert dialog will be displayed, describing the risks involved.
|
|
General Note: Predefined Policies, once chosen, cannot be modified directly from this interface - they can only be modified and defined using the 'Predefined Policies' interface. If you require the ability to add or modify settings for an specific application then you are effectively creating a new, custom policy and should choose the more flexible Use Custom Policy option instead. |
-
Use a Custom Policy - designed for more experienced users, the 'Custom Policy' option enables full control over the configuration specific security policy and the parameters of each rule within that policy. The Custom Policy has two main configuration areas - Access Rights and Protection Settings.(Default=Enabled)
In simplistic terms 'Access Rights' determine what the application can do to other processes and objects whereas 'Protection Settings' determine what the application can have done to it by other processes.
-
Access Rights - The Process Access Rights interface allows you to determine what activities the applications in your custom policy are allowed to execute. These activities are called 'Access Names'.
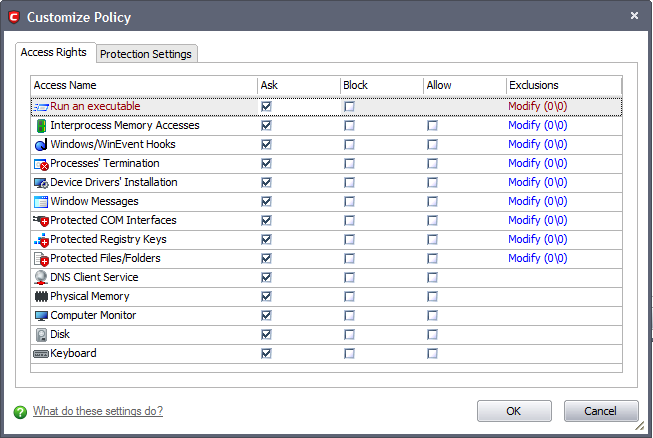
Click here to view a list of definitions of the Action Names listed above and the implications of choosing to Ask, Allow or Block for each setting.
Exceptions to your choice of 'Ask', 'Allow' or 'Block' can be specified for the policy by clicking the 'Modify' link on the right.
Select the 'Allowed Applications' or 'Blocked Applications' tab depending on the type of exception you wish to create.
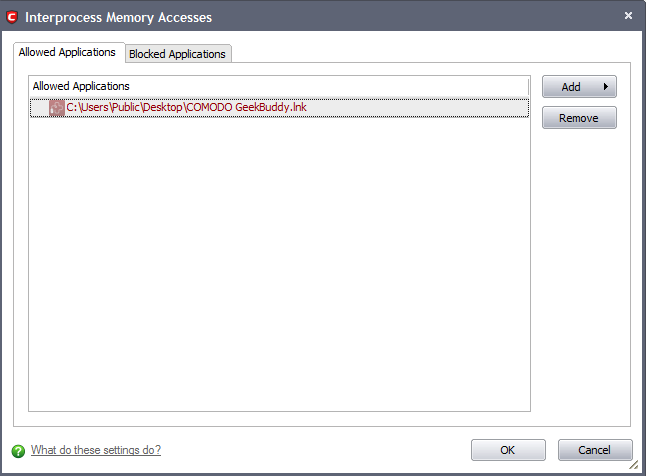
Clicking 'Add' allows you to choose which applications or file groups you wish this exception to apply to. (click here for an explanation of available options)
In the example above, the default action for 'Run as an executable' is 'Ask'. This means Defense+ generates an alert asking your permission if 'Opera.exe' tried to run another program. Clicking 'Modify' then adding 'oemig50.exe' to the 'Allowed Applications' tab creates an exception to this rule. Opera.exe is now allowed to run 'oemig50 .exe' but an alert is generated if it tries to run any other application.
-
Protection Settings - Protection Settings determine how protected the application or file group in your policy is against activities by other processes. These protections are called 'Protection Types'.
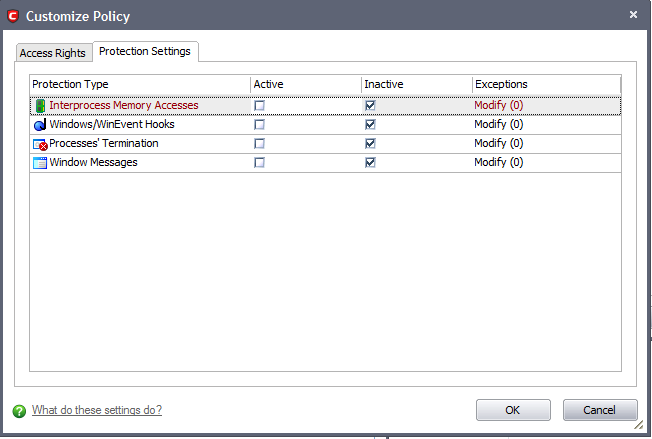
Select 'Yes' to enable monitoring and protect the application or file group against the process listed in the 'Protection Type' column. Select 'No' to disable such protection.
Click here to view a list of definitions of the 'Protection Types' listed above and the implications of activating each setting.
Exceptions to your choice of 'Yes' or 'No' can be specified in the application's policy by clicking the 'Modify...' button on the right.
-
Click 'Apply' to confirm your settings.
Comodo Internet Security User Guide | © 2012 Comodo Security Solutions Inc. | All rights reserved