Configuring Rules for Auto-Containment
The 'Auto-Containment' interface allows you to add and define rules for programs that should be run in the contained environment. A contained application has much less opportunity to damage your computer because it is run isolated from your operating system and your files. This allows you to safely run applications that you are not 100% sure about. Auto-Containment rules allow you to determine whether programs should be allowed to run with full privileges, ignored, run restricted or run in fully virtualized environment. For easy identification, Comodo Client Security will show a green border around programs that are running in the container.
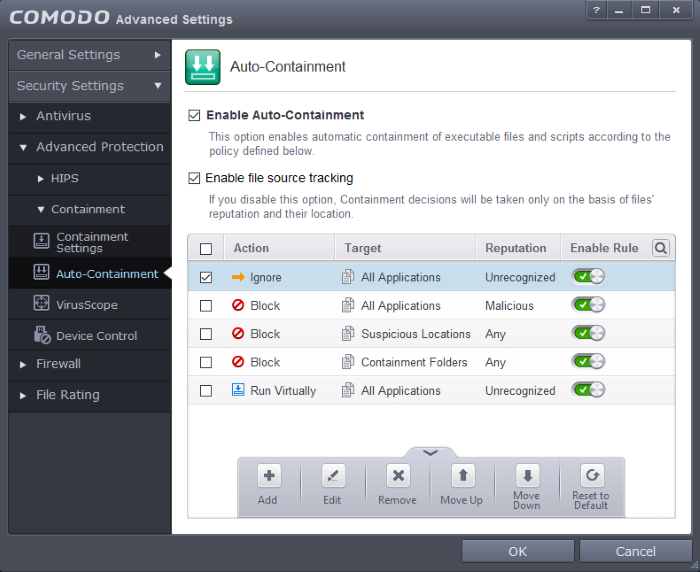
- The 'Auto-Containment' panel can be accessed by clicking 'Tasks' > 'Containment Tasks' > 'Open Advanced Settings' > 'Security Settings' > 'Containment' > 'Auto-Containment'
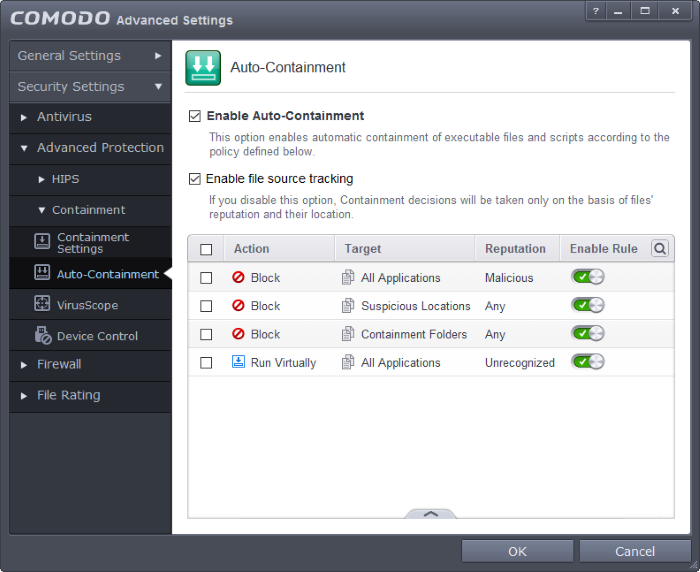
- Enable Auto-Containment - Allows you to enable or disable automatic containment of unrecognized/unknown files. If enabled, unknown applications are run inside the container as per the rules defined. (Default = Enabled)
- Enable file source tracking – If enabled, the source parameter of a containment rule will be considered. Specifying a source in a rule allows you to create granular custom rules. For example, if you wanted to only auto-contain all files downloaded from the internet, then the 'internet' is your source. If this setting is disabled then the source parameter will be disregarded and only the reputation and location parameters will be considered. More information about sources can be found here (Default = Enabled)
- Action – Displays the operation that the container should perform on the target file if the rule is triggered.
- Target – The file types, groups or locations on which the rule will be executed.
- Reputation – The trust status of the files to which the rule should apply. Can be ‘Malware’, ‘Trusted’ or ‘Unrecognized’.
- Enable Rule – Allows you to enable or disable the rule.
|
Rule |
Action |
Target |
Restriction Level |
Rating |
Source |
Log Action |
Limit Maximum memory |
Limit Program Execution Time |
Quarantine |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Created by |
Located on |
Downloaded from |
|||||||||
|
1 |
Block |
File Group - All Applications |
N/A |
Malware |
Any |
Any |
Any |
On |
N/A |
N/A |
On |
|
2 |
Block |
File Group - Suspicious Locations |
N/A |
Any |
Any |
Any |
Any |
On |
N/A |
N/A |
Off |
|
3 Applicable only for Windows 8.0 and 8.1 |
Ignore |
All Metro Apps |
Off |
Any |
Any |
Any |
Any |
On |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
4 |
Run Virtual |
File Group - All Applications |
Off |
Unrecognized |
Any |
Any |
Internet |
On |
Off |
Off |
N/A |
|
Any |
Network Drive |
Any |
|||||||||
|
Any |
Removable Drive |
Any |
|||||||||
|
5 |
Run Virtual |
File Group - All Applications |
Off |
Unrecognized |
File Group – Web Browsers |
Any |
Any |
On |
Off |
Off |
N/A |
|
File Group – Email Clients |
Any |
Any |
|||||||||
|
File Group –File Downloaders |
Any |
Any |
|||||||||
|
File Group –Pseudo-File Downloaders |
|
|
|||||||||
|
6 |
Run Virtual |
File Group – Shared Spaces |
Off |
Unrecognized |
Any |
Any |
Any |
On |
Off |
Off |
N/A |
Clicking the handle at the bottom of the interface opens a rule configuration panel:
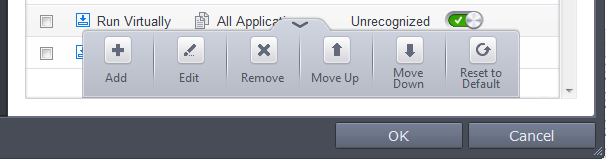
- Add - Allows you to add a new containment rule. See the section 'Adding a Auto-Containment Rule' for guidance on creating a new rule.
- Edit - Allows you to modify the selected containment rule. See the section 'Editing a Auto-Containment Rule' for more details.
- Remove - Deletes the selected rule.
- Reset to Default – Resets to default the rule.
Users can also re-prioritize the containment rules by using the 'Move Up' and 'Move Down' buttons.
Adding an Auto-Containment Rule
Auto-containment rules can be created for a single application, for all applications in a folder or file group, from running processes or for applications based on their file or process hash. ‘Source’, ‘Reputation’ and ‘Options’ allow you to add detailed filters to your rule. These are, however, optional, so you can create a very simple rule to run an application in the container just by specifying the action and the target application.
- Click the 'Add' button from the options.
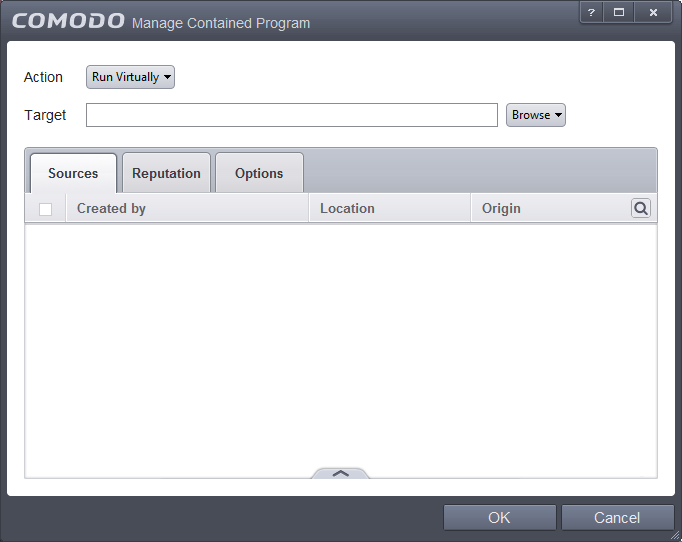
The Manage Containment Program screen will be displayed.
- Step 1 – Select the Action
- Step 2 – Select the Target
- Step 3 – Select the Sources
- Step 4 – Select the File Reputation
- Step 5 – Select the Options
The options under the 'Action' drop-down button combined with the 'Set Restriction Level' setting in the 'Options' tab determine the amount of privileges a contained application has to access other software and hardware resources on your computer.
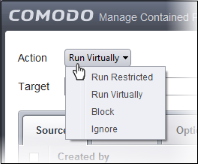
The options available are:
- Run Virtually - The application will be run in a virtual environment completely isolated from your operating system and files on the rest of your computer.
- Run Restricted - The application is allowed to access very few operating system resources. The application is not allowed to execute more than 10 processes at a time and is run with very limited access rights. Some applications, like computer games, may not work properly under this setting.
- Block - The application is not allowed to run at all.
- Ignore - The application will not be contained and is allowed to run with all privileges.
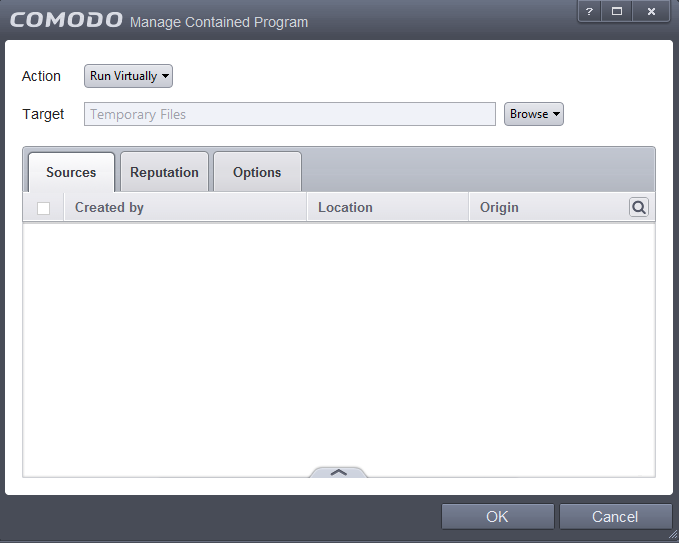
The next step is to select the target to which the auto-containment rule should be applied. Click the 'Browse' button beside the Target field.
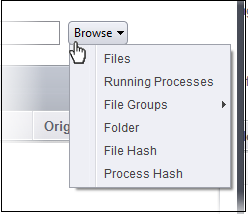
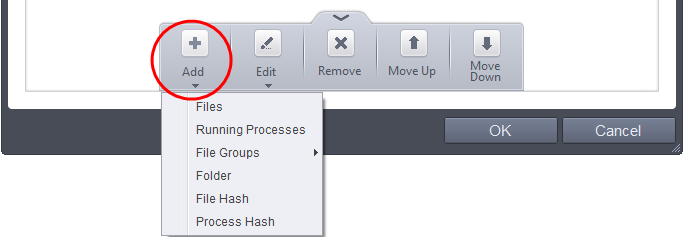
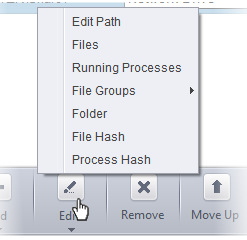
You have six options available to add the target path.
- Files – Specify individual files as targets of the rule.
- Running Processes – Add any process that is currently running on your computer as a target of the rule.
- File Groups – Add predefined file groups as the rule target. For information about creating or modifying a predefined file group, refer to File Groups.
- Folder – Allows you to add a folder or drive as the target
- File Hash – Allows you to add a file as target based on its hash value
- Process Hash - Allows you to add any process that is currently running on your computer as a target based on its hash value
-
Choose 'Files' from the 'Browse' drop-down.
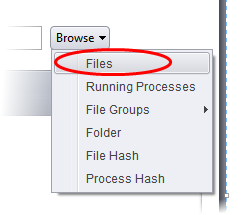
-
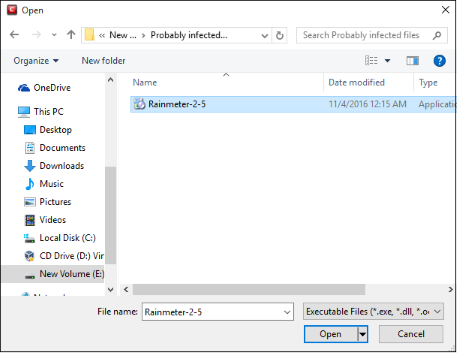
Navigate to the file you want to add as target in the 'Open' dialog and click 'Open'
The file will be added as target and will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
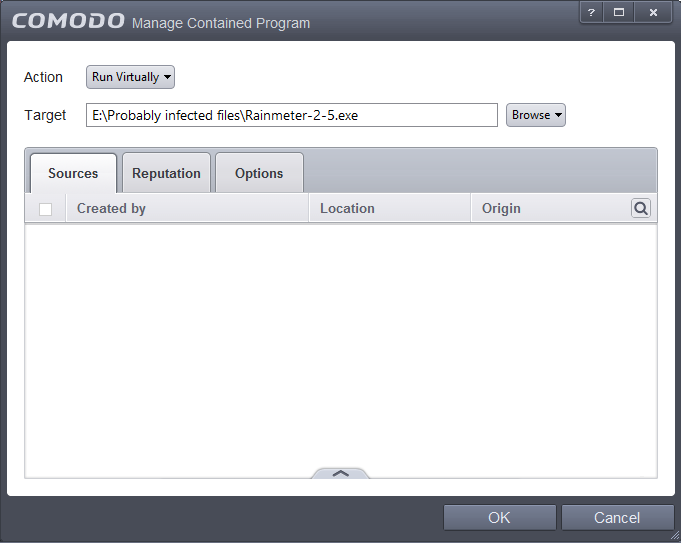
If you want to just add an application for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
Adding an application from a running processes
-
Choose 'Running Processes' from the 'Browse' drop-down.
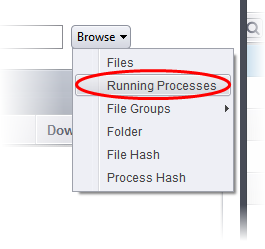
A list of currently running processes in your computer will be displayed.
-
Select the process, whose target application is to be added to target and click 'OK' from the Browse for Process dialog.
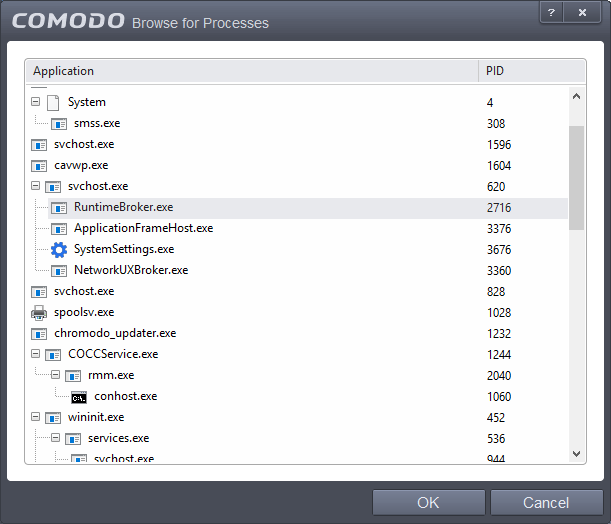
The file will be added as target and will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
If you want to just add an application for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
-
Choose 'File Groups' from the 'Browse' drop-down. Choosing File Groups allows you to include a category of pre-set files or folders. For more details on how to manage file groups refer to the section File Groups.
-
Select the preset file group from the options.
-
The file group will be added as target and the applications inside it will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
If you want to just add the applications in the file group for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
Adding a Folder/Drive Partition
-
Choose 'Folder' from the 'Browse' drop-down.
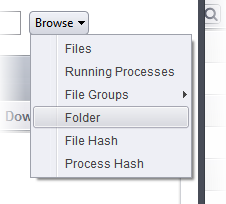
The 'Browse for Folder' dialog will appear.
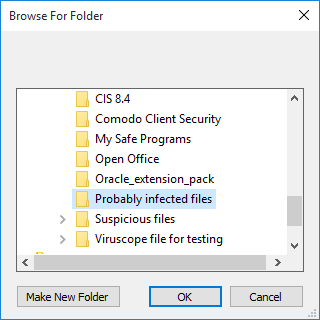
-
Navigate to the drive partition or folder you want to add as target and click 'OK'
The drive partition/folder will be added as target and will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
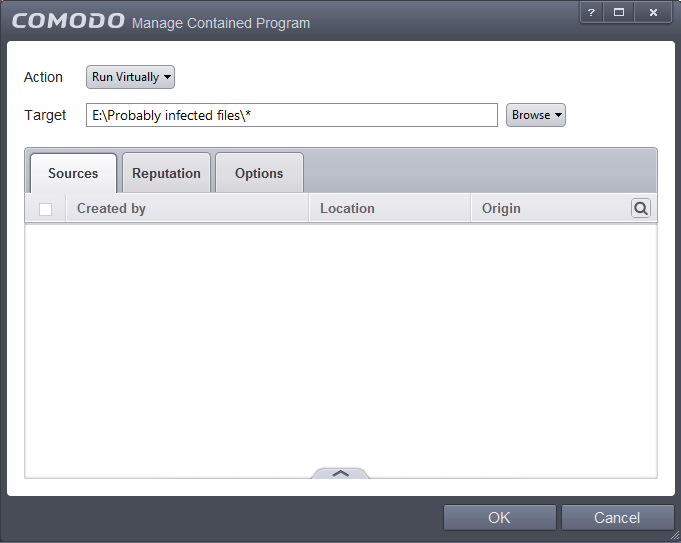
If you want to just add the applications in the drive partition/folder for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
Adding a file based on its hash value
-
Choose 'File Hash' from the 'Browse' drop-down.
-
Navigate to the file whose hash value you want to add as target in the 'Open' dialog and click 'Open'
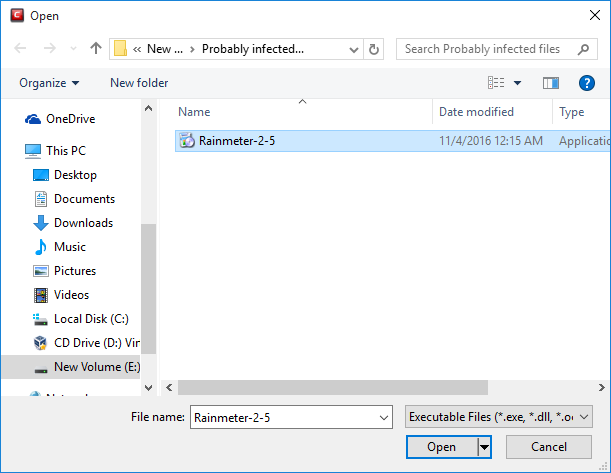
The file will be added as target and will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
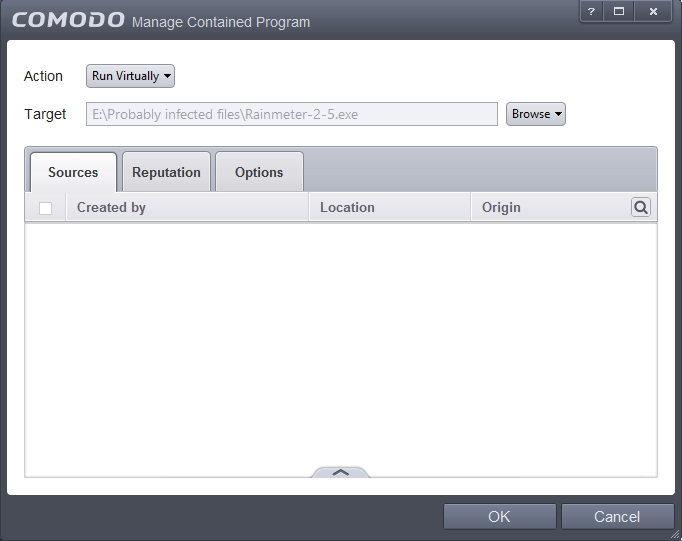
If you want to just add the hash value of an application for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
Adding an application from a running process based on its hash value
-
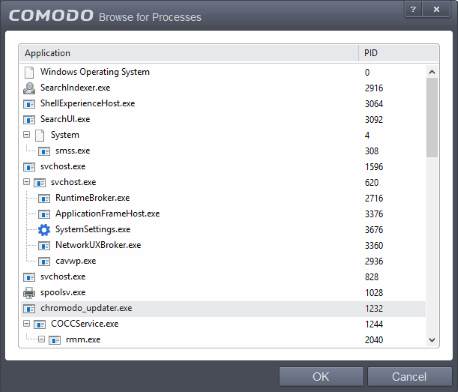
Choose 'Process Hash' from the 'Browse' drop-down.
A list of currently running processes in your computer will be displayed.
-
Select the process, whose hash value of the target application is to be added to target and click 'OK' from the Browse for Process dialog.
The file will be added as target and will be run as per the action chosen in Step 1.
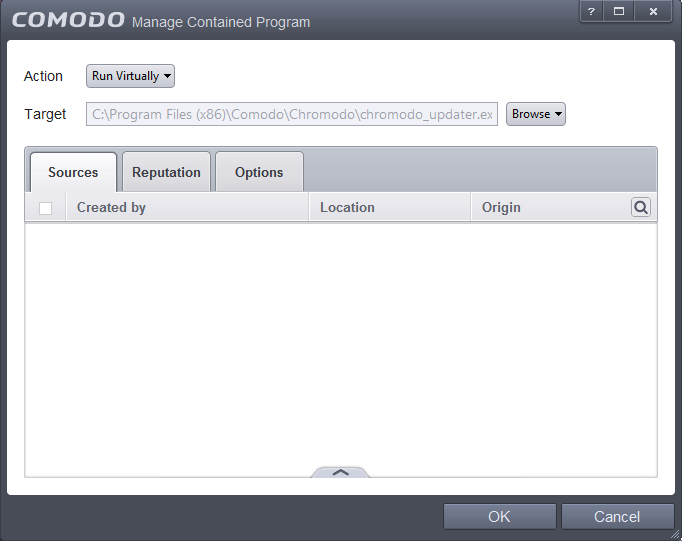
If you want to just add the process hash value of an application for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying any filters or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Sources and Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Source and Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
If you want to include a number of items in a rule but want the rule to be applied only in certain conditions, then you can do so in this step. For example, if you want your target to be executables downloaded from the internet, then you would add 'All Applications' then apply a filter in 'Sources' tab. Another example is you want to exclude from containment any unrecognized files from your internal network share. You could create an ignore rule with 'All Applications' set as the target and specify your source as your intranet.
Please note that the 'Enable file source tracking' check box should be enabled in the 'Auto-Containment' screen for the source parameter to be taken account in the rule. If this is not enabled then the source parameter will be ignored and the rule will be applied based on the other parameters.
To add a source
-
Click the handle at the bottom and then click Add from the options.
The options available are available same as explained in Step 2.
The following example describes how to add an 'Ignore' rule for Unrecognized files from a network source:
- In Step 1, select the action as Ignore
- In Step 2, select the Target as File Groups > All Applications
- In Step 3, click the 'Add' options. Navigate to the source folder on the network and click 'OK'.
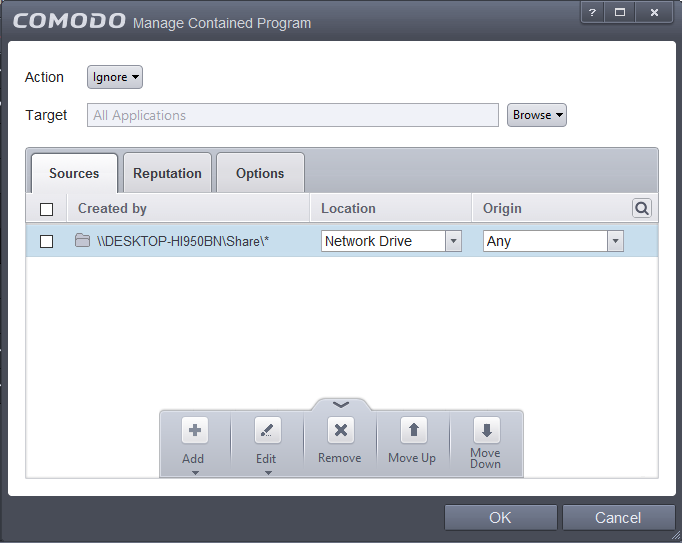
The selected network source folder will be added under the 'Created by' column and the screen displays the options to specify the location and from where the files were downloaded.
- Location – Apply the rule to files found in one of the following locations:
- Any
- Local Drive
- Removable Drive
- Network Drive
Since the source is located in a network, select Network Drive from the options.
- Origin – The options available are:
- Any – The rule will apply to files that were downloaded to the source folder from both Internet and Intranet.
- Internet – The rule will apply to files that were downloaded to the source folder from Internet only.
- Intranet – The rule will apply to files that were downloaded to the source folder from Intranet only.
Repeat the process to add more source folders.
-
Click the 'Edit' button to change the source path from the options:
- To remove a source from the list, select it and click the Remove button.
- Use the 'Move Up' and 'Move Down' buttons to specify the order of source path.
If you want to just add the Sources for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying rating of the file or options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Reputation will be 'Any' and for Options it will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Reputation filters and Options for the rule.
Since the example rule is created for files that are categorized as Unrecognized, the same has to be selected from the rating options in Step 4.
Step 4 – Select the File Reputation
- Click the 'Reputation' tab in the 'Manage Contained Program' interface.
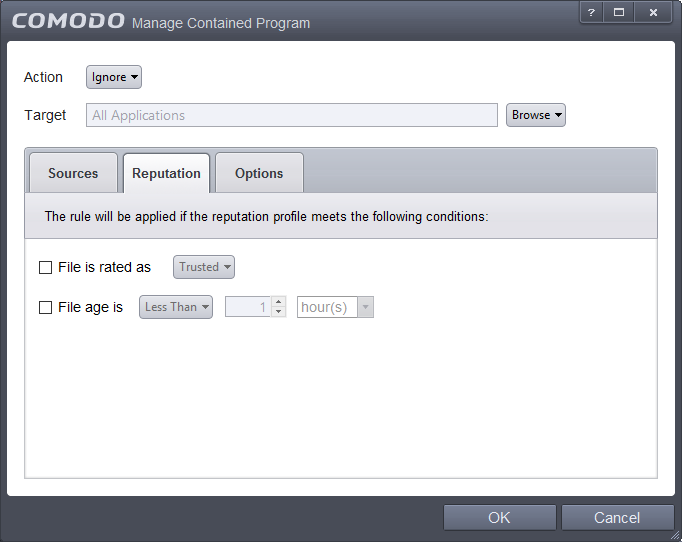
By default, the file rating is not selected meaning the rating could be Any. The options available are:
- Trusted – Applications that are signed by trusted vendors and files installed by trusted installers are categorized as Trusted files by CCS. Refer to the sections File Rating Settings and Files List for more information.
- Unrecognized – Files that are scanned against the Comodo safe files database not found in them are categorized as Unrecognized files. Refer to the section Files List for more information.
- Malware – Files are scanned according to a set procedure and categorized as malware if not satisfying the conditions. Refer the section Unknown Files: The Scanning Process for more information.
By default, file age is not selected, so the age could be Any. The options available are:
- Less Than – CCS will check for reputation if a file is younger than the age you set here. Select the interval in hours or days from the first drop-down combo box and set hours or days in the second drop-down box. (Default and recommended = 1 hour)
- More Than - CCS will check for reputation if a file is older than the age you set here. Select the interval in hours or days from the first drop-down combo box and set hours or days in the second drop-down box. (Default and recommended = 1 hour)
Select the category from the options. Since the example rule is created for files that are categorized as Unrecognized, the same has to be selected from the rating options.
If you want to just add the Sources and Reputation for a particular action as selected in Step 1 without specifying the options, then click 'OK'. The default values for Options will be 'Log when this action is performed'. If required you can configure Options for the rule.
- Click the Options tab in the 'Manage Contained Program' interface.
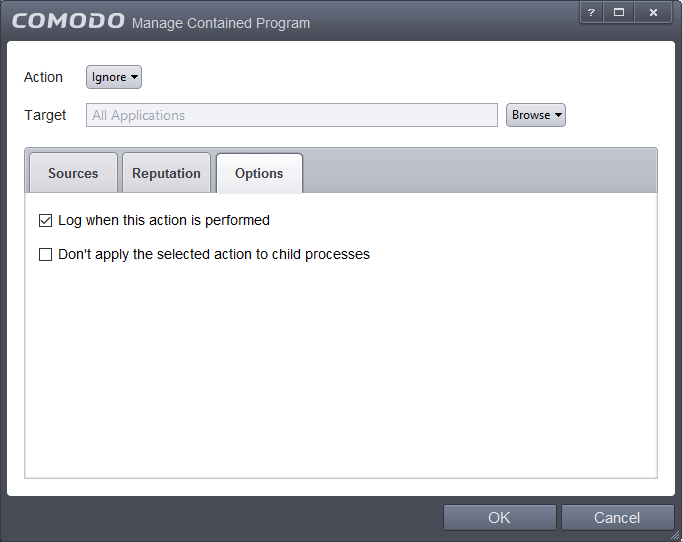
By default, the 'Log when this action is performed' The options available for Ignore action are:
- Log when this action is performed – Whenever this rule is applied for the action, it will be logged.
- Don't apply the selected action to child processes – Child processes are the processes initiated by the applications. For example, the process may launch another app or plugin. CCS treats all child processes as individual processes and forces them to run as per their file rating and the containment rules.
- This option is disabled by default, so the ignore rule will usually be applied to all child process of the target application(s).
- If this option is enabled, then the Ignore rule will be applied only to the target application. All child processes will be checked individually and containment rules applied as per the child's file rating.
- The 'Don't apply to child processes' option is available only for the 'Ignore' action. For 'Run Restricted' and 'Run Virtually', the following options are available:
- Log when this action is performed – Whenever this rule is applied for the action, it will be logged.
- Set Restriction Level – When Run Restricted is selected in Action, then this option is automatically selected and cannot be unchecked while for Run Virtually action the option can be checked or unchecked. The options for Restriction levels are:
- Partially Limited - The application is allowed to access all operating system files and resources like the clipboard. Modification of protected files/registry keys is not allowed. Privileged operations like loading drivers or debugging other applications are also not allowed. (Default)
- Limited - Only selected operating system resources can be accessed by the application. The application is not allowed to execute more than 10 processes at a time and is run without Administrator account privileges.
- Restricted - The application is allowed to access very few operating system resources. The application is not allowed to execute more than 10 processes at a time and is run with very limited access rights. Some applications, like computer games, may not work properly under this setting.
- Untrusted - The application is not allowed to access any operating system resources. The application is not allowed to execute more than 10 processes at a time and is run with very limited access rights. Some applications that require user interaction may not work properly under this setting.
- Limit maximum memory consumption to – Enter the memory consumption value in MB that the process should be allowed.
- Limit program execution time to – Enter the maximum time in seconds the program should run. After the specified time, the program will be terminated.
For Block action, the following options are available:
- Log when this action is performed – Whenever this rule is applied for the action, it will be logged.
- Quarantine program – If checked, the programs will be automatically quarantined. Refer to the section Manage Quarantined Items for more information.
Choose the options and click 'OK'. The rule will be added and displayed in the list.
Editing an Auto-Containment Rule
- To edit an auto-containment rule, select it from the list and click 'Edit' from the options.
The Manage Contained Program interface will be displayed. The procedure is similar to adding Adding an Auto-Containment Rule.
- Click 'OK' to save the changes to the rule.
|
Important Note: Please make sure the auto-containment rules do not conflict. If it does conflict, the settings in the rule that is higher in the list will prevail. |



